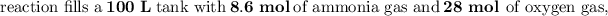
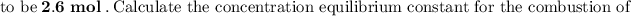
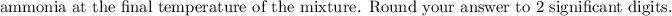
Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
From the correct question above:
The reaction can be represented as:
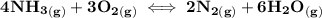
From the above reaction; the ICE table can be represented as:
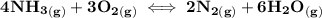
I (mol/L) 0.086 0.28 0 0
C -4x -3x +2x +6x
E 0.086 - 4x 0.28 - 3x +2x +6x
At equilibrium;
The water vapor =
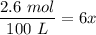
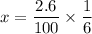
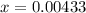
![\text{equilibrium constant} ({k_c}) = ( [N_2]^2 [H_2O]^6 )/( [[NH_3]^4] [O_2]^3 )](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/n2oj6b7v7nm663s11s2ub9uwc49ahji6ll.png)
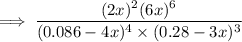
Replacing the value of x, we have: