Answer:
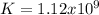
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello there!
Unfortunately, the question is not given in the question; however, it is possible for us to compute the equilibrium constant as the problem is providing the concentrations at equilibrium. Thus, we first set up the equilibrium expression as products/reactants:
![K=([NO_2]^2)/([NO]^2[O_2])](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/high-school/dp77ty81xjtltu43wzw7yricmd5dzbbhsp.png)
Then, we plug in the concentrations at equilibrium to obtain the equilibrium constant as follows:
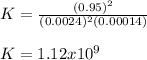
In addition, we can infer this is a reaction that predominantly tends to the product (NO2) as K>>>>1.
Best regards!