Answer: 1.
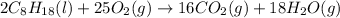
2. The volume of carbon dioxide gas that is produced is 537 L
Step-by-step explanation:
1. Combustion is defined as the type of chemical reaction where a hydrocarbon is combusted in the presence of oxygen to give carbon dioxide and water.
The balanced reaction for combustion of octane is:
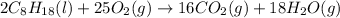
2.
To calculate the moles :
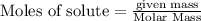
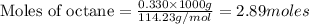
According to stoichiometry:
2 moles of octane produce = 16 moles of carbon dioxide
2.89 moles of octane produce =
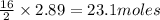 of carbon dioxide
of carbon dioxide
According to ideal gas equation:
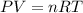
P = pressure of gas = 1 atm
V = Volume of gas = ?
n = number of moles = 23.1
R = gas constant =
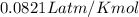
T =temperature =
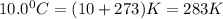
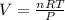
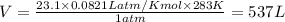
Thus the volume of carbon dioxide gas that is produced is 537 L