Answer: The standard potential is -0.141 V
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the Gibbs free energy for given value of equilibrium constant we use the relation:
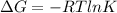
where,
= standard Gibbs free energy = ?
R = Gas constant = 8.314 J/Kmol
T = temperature = 298 K
K = equilibrium constant =
Putting values in above equation, we get:
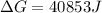
Also

where n = no of electrons gained or lost = 3
F = Faradays constant = 96500 C
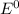 = standard potential = ?
= standard potential = ?
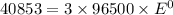
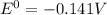
Thus the standard potential is -0.141 V