Answer:
0.682 = 68.2% probability that the average length of these 16 shells will be between 116 and 120 centimeters when the machine is operating "properly".
Explanation:
To solve this question, we need to understand the normal probability distribution and the central limit theorem.
Normal Probability Distribution:
Problems of normal distributions can be solved using the z-score formula.
In a set with mean
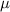 and standard deviation
and standard deviation
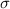 , the z-score of a measure X is given by:
, the z-score of a measure X is given by:
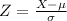
The Z-score measures how many standard deviations the measure is from the mean. After finding the Z-score, we look at the z-score table and find the p-value associated with this z-score. This p-value is the probability that the value of the measure is smaller than X, that is, the percentile of X. Subtracting 1 by the p-value, we get the probability that the value of the measure is greater than X.
Central Limit Theorem
The Central Limit Theorem estabilishes that, for a normally distributed random variable X, with mean
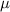 and standard deviation
and standard deviation
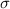 , the sampling distribution of the sample means with size n can be approximated to a normal distribution with mean
, the sampling distribution of the sample means with size n can be approximated to a normal distribution with mean
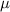 and standard deviation
and standard deviation
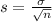 .
.
For a skewed variable, the Central Limit Theorem can also be applied, as long as n is at least 30.
Normally distributed with a mean of 118 centimeters and a standard deviation of 8 centimeters.
This means that
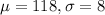
Sample of 16 shells
This means that
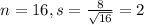
What is the probability that the average length of these 16 shells will be between 116 and 120 centimeters when the machine is operating "properly?"
This is the pvalue of Z when X = 120 subtracted by the pvalue of Z when X = 116.
X = 120
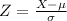
By the Central Limit Theorem
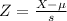
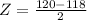
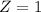
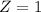 has a pvalue of 0.841
has a pvalue of 0.841
X = 116
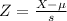
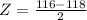
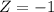
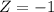 has a pvalue of 0.159
has a pvalue of 0.159
0.841 - 0.159 = 0.682
0.682 = 68.2% probability that the average length of these 16 shells will be between 116 and 120 centimeters when the machine is operating "properly".