Answer:
a) S = {(1,2), (1,3), (1,4), (1,5), (2,3), (2,4), (2,5), (3,4), (3,5), (4,5)}
b) p(x) = 0.3 if x = 0
= 0.6 if x = 1
= 0.1 if x = 2
= 0 otherwise
Explanation:
Given - Many manufacturers have quality control programs that include inspection of incoming materials for defects. Suppose a computer manufacturer receives computer boards in lots of five. Two boards are selected from each lot for inspection. We can represent possible outcomes of the selection process by pairs. For example, the pair (1, 2) represents the selection of boards 1 and 2 for inspection.
To find - (a) List the ten different possible outcomes.
(b) Suppose that boards 1 and 2 are the only detective boards in a lot of five. Two boards are to be chosen at random. Define X to be the # of defective boards observed among those inspected. Find the pmf.
Proof -
(a)
Given that there are 5 computer boards
Let,
The Boards are 1, 2, 3, ,4 and 5.
Now,
Total Number of possible ways of selecting 2 boards out of 5 by inspection = ⁵C₂ =
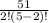 =
=
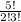 =
=
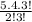 =
=
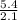 = 10
= 10
And the choices be
Choice I -
Boards 1 and Board 2
Choice II -
Board 1 and Board 3
Choice III -
Board 1 and Board 4
Choice IV -
Board 1 and Board 5
Choice V -
Board 2 and Board 3
Choice VI -
Board 2 and Board 4
Choice VII -
Board 2 and Board 5
Choice VIII -
Board 3 and Board 4
Choice IX -
Board 3 and Board 5
Choice X -
Board 4 and Board 5
And
These outcomes becomes
S = {(1,2), (1,3), (1,4), (1,5), (2,3), (2,4), (2,5), (3,4), (3,5), (4,5)}
(b)
Given that, X be the number of defective boards
And there are only two defective boards (Board 1 and Board 2) in the lot
Therefore,
X can be 0, 1, and 2.
Now,
If X = 0
⇒ There is no defective boards
⇒ Possible outcomes be - { (3,4), (3,5), (4,5) }
So,
P(X=0) =
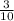 = 0.3
= 0.3
Now,
If X = 1
⇒ There is one defective board
⇒ Possible outcomes be - { (1,3), (1,4), (1,5), (2,3), (2,4), (2,5) }
So,
P(X=1) =
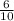 = 0.6
= 0.6
Now,
If X = 2
⇒ There is two defective boards
⇒ Possible outcomes be - { (1,2) }
So,
P(X=2) =
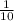 = 0.1
= 0.1
And
P(x) = 0 if x ≠ 0, 1, 2
SO, The pmf be
p(x) = 0.3 if x = 0
= 0.6 if x = 1
= 0.1 if x = 2
= 0 otherwise