Hi there!
We can find the compressed distance by using the equation for Spring Potential Energy:
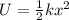
U = Potential Energy (3.2 J)
k = Spring Constant (529 N/m)
x = Compression distance (? m)
Rearrange and solve for 'x'.
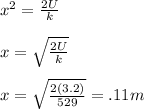
Now, we can find the velocity using the Work-Energy theorem. There is work done by friction in this instance, however.
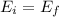
Initially, there is only Spring Potential Energy. Then, some of that energy is converted to kinetic energy, while some is lost to friction.
Thus:
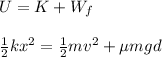
Rearrange to solve for velocity.
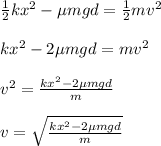
Plug in the values and solve. (d = compression distance)
