Answer:
n = 1.14 mol
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello there!
In this case, according to the ideal gas law:
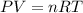
It is possible to solve for the moles of the gas given the volume, temperature and pressure:
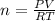
Thus, we plug in 14.0 L, 300 K and 2.0 atm to obtain:
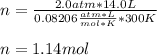
Best regards!