Answer:
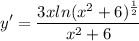
General Formulas and Concepts:
Pre-Algebra
Order of Operations: BPEMDAS
- Brackets
- Parenthesis
- Exponents
- Multiplication
- Division
- Addition
- Subtraction
Algebra I
Calculus
Derivatives
Derivative Notation
Derivative of a constant is 0
Basic Power Rule:
- f(x) = cxⁿ
- f’(x) = c·nxⁿ⁻¹
Derivative Property [Multiplied Constant]:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx) [cf(x)] = c \cdot f'(x)](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/rwpyhrof52dro5d128gleq5obchnuu5qkj.png)
Derivative Rule [Chain Rule]:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx)[f(g(x))] =f'(g(x)) \cdot g'(x)](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/vue68srn3fe6bds4idxorm97z7tgwelamw.png)
ln Derivative:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx) [lnu] = (u')/(u)](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/zf0m3fv68j30cbn0bslnu5admdwd4laga9.png)
Explanation:
Step 1: Define
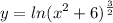
Step 2: Differentiate
- [Derivative] Chain Rule:
![\displaystyle y' = (d)/(dx)[ln(x^2 + 6)^{(3)/(2)}] \cdot (d)/(dx)[ln(x^2 + 6)] \cdot (d)/(dx)[x^2 + 6]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/spckbl1lieei4ot70f5vr1x6svfxgpur63.png)
- [Derivative] Chain Rule [Basic Power Rule]:
![\displaystyle y' = (3)/(2)ln(x^2 + 6)^{(3)/(2) - 1} \cdot (d)/(dx)[ln(x^2 + 6)] \cdot (d)/(dx)[x^2 + 6]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/ufjqx0p8yim408ek7rjk0r09pbvz84bj3z.png)
- [Derivative] Simplify:
![\displaystyle y' = (3)/(2)ln(x^2 + 6)^{(1)/(2)} \cdot (d)/(dx)[ln(x^2 + 6)] \cdot (d)/(dx)[x^2 + 6]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/q2groqnhvtm07pyqzogj2qj8jvin2b38ml.png)
- [Derivative] ln Derivative:
![\displaystyle y' = (3)/(2)ln(x^2 + 6)^{(1)/(2)} \cdot (1)/(x^2 + 6) \cdot (d)/(dx)[x^2 + 6]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/sfz4tkjo3abnf17uwxcsyp7fv0hb742u5d.png)
- [Derivative] Basic Power Rule:
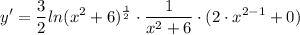
- [Derivative] Simplify:
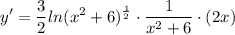
- [Derivative] Multiply:
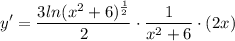
- [Derivative] Multiply:
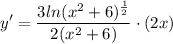
- [Derivative] Multiply:
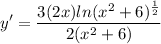
- [Derivative] Multiply:
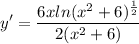
- [Derivative] Factor:
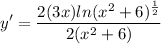
- [Derivative] Simplify:
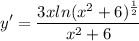
Topic: AP Calculus AB/BC (Calculus I/II)
Unit: Derivatives
Book: College Calculus 10e