Answer:
The force acting on the object at
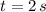 is
is
![\vec F = (4, 32)\,[N]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/physics/college/cypi73hhkk9883iew7n9kigicwwo93k3tr.png) .
.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that object has a constant mass in time, the force acting on the object (
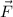 ), in newtons, is defined by following expression:
), in newtons, is defined by following expression:
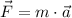 (1)
(1)
Where:
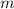 - Mass, in kilograms.
- Mass, in kilograms.
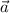 - Acceleration, in meters per square second.
- Acceleration, in meters per square second.
By definition of acceleration, we know that:
 (2)
(2)
Let suppose that given vector velocity is expressed in meters per second. If we know that
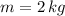 ,
,
![\vec v = (2\cdot t, 4\cdot t^(2))\,\left[(m)/(s) \right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/physics/college/lakrrw5d117x6ux1ory89knu09l4ox3n6r.png) and
and
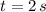 , then the force acting on the object is:
, then the force acting on the object is:
![\vec a = (2, 8\cdot t)\,\left[(m)/(s^(2)) \right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/physics/college/xwv92zbzut8ae2axzdca1tjzu1teer1saj.png)
![\vec F = (4, 16\cdot t)\,[N]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/physics/college/gni7ntxktv6cnponni92i0ox1lvrtsl0et.png)
![\vec F = (4, 32)\,[N]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/physics/college/cypi73hhkk9883iew7n9kigicwwo93k3tr.png)
The force acting on the object at
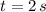 is
is
![\vec F = (4, 32)\,[N]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/physics/college/cypi73hhkk9883iew7n9kigicwwo93k3tr.png) .
.