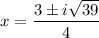Answer:
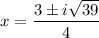
General Formulas and Concepts:
Pre-Algebra
Order of Operations: BPEMDAS
- Brackets
- Parenthesis
- Exponents
- Multiplication
- Division
- Addition
- Subtraction
Algebra I
- Standard Form: ax² + bx + c = 0
- Factoring
- Quadratic Formula:
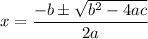
Algebra II
- Imaginary Numbers: i = √-1
Explanation:
Step 1: Define
2x² - 3x + 6 = 0
Step 2: Solve for x
- [Quadratic] Identify Variables [Standard Form]: a = 2, b = -3, c = 6
- Substitute in variables [Quadratic Formula]:
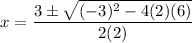
- [√Radical] Evaluate exponents:
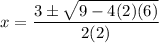
- [√Radical] Multiply:
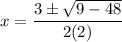
- [√Radical] Subtract:
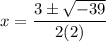
- Multiply:
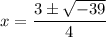
- Factor:
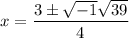
- Simplify: