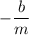Answer:
The y-intercept is when x = 0 (where the line crosses the y-axis), so look for the constant in the equation (without a variable).
For example, the y-intercept for the equation y = 2x + 4 is 4.
The y-intercept for the equation y = 3x² - 6x + 8 is 8.
The x-intercept is when y = 0 (where the line crosses the x-axis). This can be trickier to find (without simply setting the equation to zero and solving for x), depending on the type of equation.
If the equation is a polynomial that can be factored, then the x-intercepts are easier to spot, as each of the factors equals zero.
For example, the x-intercepts for the equation y = x(x - 2)(x + 3)(x - 1) are 0, 2, -3 and 1 as (x - 2) = 0 so x = 2 and so on.
For a linear equation in the form y = mx + b the x-intercept would be