Answer:
q_metal = -12000 J = -12 KJ
Here, the negative sign indicates that the energy is lost by the metal piece.
Step-by-step explanation:
The magnitude of energy change of the metal X can be given by the following formula:
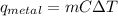
where,
m = mass of metal = 100 g
C = Specific Heat Capacity of metal X = 0.24 J/g.°C
ΔT = Change in Temperature of Metal Piece = 0° C - 500°C = -500°C
Therefore, using these values in the equation, we get:
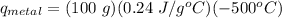
q_metal = -12000 J = -12 KJ
Here, the negative sign indicates that the energy is lost by the metal piece.