Answer:
Explanation:
Null hypothesis:
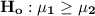
Alternative hypothesis:
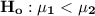
This type of test statistic is a z test statistics
1st 2nd
Sample mean x = 112.2 117,8
Standard deviation σ = 14.0 14.5
Sample size n = 95 70
Point estimate
 = -5.60
= -5.60
Standard error
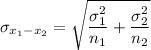
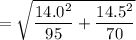 = 2.2509
= 2.2509
Test statistics
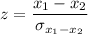
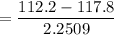 = - 2.4878
= - 2.4878
P-value = 0.012
No, there is no enough evidence Since p-value is greater than 0.01.