Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
The molecular formula for Guanylate is
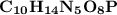
This is calculated by the addition of the atomic weight of all the atoms taking part in the molecule.
i.e. (10 × C) + (14 × H) + (5 × N) + ( 8 × O) + (1 × P)
= (10 × 12) + (14 × 1) + (5 × 14) + ( 8 × 16) + (1 × 30)
= 120 + 14 + 70 + 128 + 30
= 362 g/mol
The diagram for the tautomers of hypoxanthine can be seen in the image attached below.
Dihydrouridine is available and can be seen in tRNAs and rRNAs. It is an exceptionally preserved and adjusted base. It is a pyrimidine nucleoside that is shaped by the expansion of two hydrogen atoms to uridine. By the expansion of two hydrogen atoms to uridine makes it completely soaked and no presence of any two-fold or double bond.
Catalytic reduction of carbon-carbon double bonds in Dihydrouridine synthase occurs at positions 5 and 6 on the uridine base.
Hence, 5 and 6 carbon particles inside the uracil moiety of this nucleotide have two hydrogens each connected to them.