Answer:
E = 216.76 J
Step-by-step explanation:
The amount of energy absorbed by the goalkeeper will be equal to the difference between the initial and the final kinetic energy of the ball.
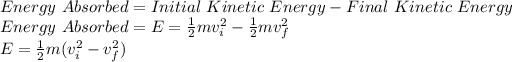
where,
m = mass of ball = (16 ounce)(0.0283495 kg/1 ounce) = 0.4535 kg
vf = final velocity = 2.25 m/s
vi = initial velocity = 31 m/s
Therefore,
![E = (1)/(2)(0.4535\ kg)[(31\ m/s)^2 - (2.25\ m/s)^2]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/physics/college/y8yqgf8m0oy7cgzstnrnvn1kca16euymm3.png)
E = 216.76 J