Answer:
The magnitude of the magnetic force on the rod is 0.037 N.
Step-by-step explanation:
The magnetic force is given by:
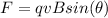
Since the charge (q) is:
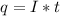
Where I is the current = 1.40 A, and t the time
And the speed (v):
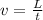
Where L is the tracks separation = 2.20 cm = 0.022 m
Hence, the magnetic force is:
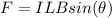
Where B is the magnetic field = 1.20 T and θ is the angle between the tracks and the magnetic field = 90°
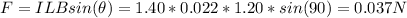
Therefore, the magnitude of the magnetic force on the rod is 0.037 N.
I hope it helps you!