Answer:
-96
Explanation:
Given:
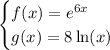
To find g[f(-2)], substitute x = -2 into the function f(x):
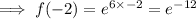
Then substitute the function f(-2) in place of the x in function g(x):
![\implies g[f(-2)]=8 \ln \left(e^(-12)\right)](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/9o10qoiq579qrrs5k7p24yblemwpkpinkc.png)
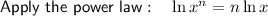
![\begin{aligned}\implies g[f(-2)]&=-12\cdot 8 \ln \left(e\right)\\&=-96 \ln \left(e\right)\end{aligned}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/tqcuz9cr20rucu5zgygmyt5xcu4rkt9bg8.png)
Apply the log law: ln(e) = 1
![\begin{aligned}\implies g[f(-2)]&=-96 \ln \left(e\right)\\&=-96(1)\\&=-96\end{aligned}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/1bkkh01llm6e2mjnpl713xc31p10et4u5j.png)
---------------------------------------------------------------------
As one calculation:
![\begin{aligned}g[f(-2)]&=8 \ln \left(e^(6 * -2)\right)\\& = 8 \ln \left(e^(-12)\right)\\& = -12 \cdot 8 \ln \left(e\right)\\& = -96(1)\\& = -96\end{aligned}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/zyx4w67xyuzgfrte0g9hp4gky0vgvnrrgn.png)