We are asked to find the first derivative of,
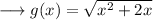
Here we can write the term
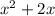 by adding and subtracting 1 as,
by adding and subtracting 1 as,
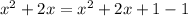
![x^2+2x = (x+1)^2-1\quad[\because\, x^2+2x+1=(x+1)^2]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/cdn5l5fwdtd8wxw71l04xu55vpf4in7p37.png)
Thus,
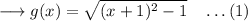
Now take,
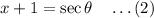
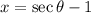
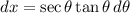
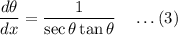
Then (1) becomes,
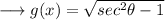
We have,
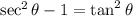
So we get,
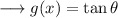
Now,
![\longrightarrow g'(x) = (d)/(dx)\,[\tan\theta]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/dolzziin5rb2wfqbar0tc6eucdnnjngbk0.png)
By chain rule,
![\longrightarrow g'(x) = (d)/(d\theta)\,[\tan\theta]\cdot(d\theta)/(dx)](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/6ieqmjtjhp7yofu35a8udxrwqu06g7zsh1.png)
![\longrightarrow g'(x) = \sec^2\theta\cdot(1)/(\sec\theta\tan\theta)\quad\quad\textrm{[From (3)]}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/t35tbrth0mlahprjj1b4s35a167agne9y7.png)
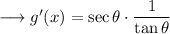
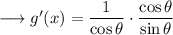
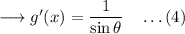
But we have,
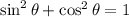
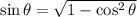
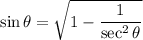
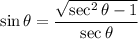
![\sin\theta=(√((x+1)^2-1))/(x+1)\quad\quad\textrm{[From (2)]}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/9uv19ust7s43bin8inm67ajo6ibxxx5xhv.png)
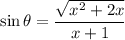
Hence (4) becomes,
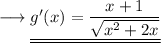
This is the first derivative of the given function.