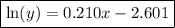Answer:
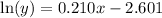
Explanation:
Given table:
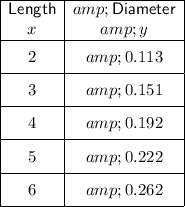
To convert y = abˣ to linear form, take natural logs of both sides and rearrange:
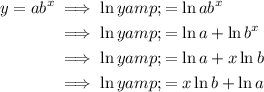
This is in the straight-line form y = mx + c.
Substitute the first and last values of x and y from the table into the natural log formula:
Subtract the first equation from the second equation to eliminate ln(a);
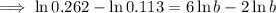
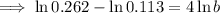
Apply the quotient log law:
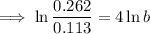
Rearrange and solve for ln(b):
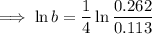
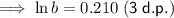
Substitute the found value of ln(b) into one of the equations and solve for ln(a):
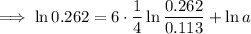
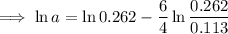
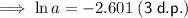
Substitute the found values of ln(a) and ln(b) into the formula to create an equation for ln(y):