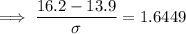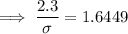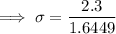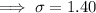Answer:
Standard deviation σ = 1.40 (2 d.p.)
Explanation:
If a continuous random variable X is normally distributed with mean μ and variance σ², it is written as:
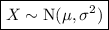
Given:
- Mean μ = 13.9 g/dL
- P(X < 16.2) = 0.95
Therefore, if the haemoglobin levels are normally distributed:
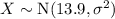
where X is the haemoglobin level.
Converting to the Z distribution:
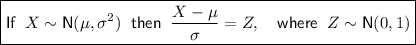
Transform X to Z:
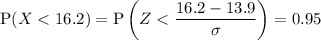
According to the z-tables, when p = 0.95, z = 1.6449