Answer:
Function I
Explanation:
Differentiate each function.
Function I
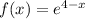
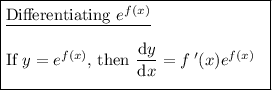
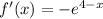
The domain of f'(x) is all real numbers: (-∞, ∞)
Therefore f(x) is differentiable for all values of x over the interval (-5, 5).
Function II
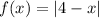

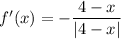
The domain of f'(x) is all real numbers except x = 4: (-∞, 4) ∪ (4, ∞)
Therefore, f(x) is not differentiable for all values of x over the interval (-5, 5).
Function III
![\begin{aligned}f(x)&=\sqrt[3]{4-x}\\&=(4-x)^{(1)/(3)}\end{aligned}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/fn4ypfeksfl273wryabh87xgsuosufzptr.png)
![\boxed{\begin{minipage}{7 cm}\underline{Differentiating $[f(x)]^n$}\\\\If $y=[f(x)]^n$, then $\frac{\text{d}y}{\text{d}x}=n[f(x)]^(n-1) f'(x)$\\\end{minipage}}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/ru6yqsooqddix160q9uosrb7y4hacb089p.png)
Therefore:
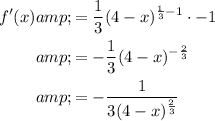
The domain of f'(x) is all real numbers except x = 4: (-∞, 4) ∪ (4, ∞)
Therefore, f(x) is not differentiable for all values of x over the interval (-5, 5).
Function 4
![\boxed{\begin{minipage}{7 cm}\underline{Differentiating $[f(x)]^n$}\\\\If $y=[f(x)]^n$, then $\frac{\text{d}y}{\text{d}x}=n[f(x)]^(n-1) f'(x)$\\\end{minipage}}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/ru6yqsooqddix160q9uosrb7y4hacb089p.png)
Therefore:
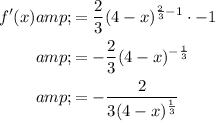
The domain of f'(x) is all real numbers except x = 4: (-∞, 4) ∪ (4, ∞)
Therefore, f(x) is not differentiable for all values of x over the interval (-5, 5).