Answer:
a) 314
b) 64%
Explanation:
If a continuous random variable X is normally distributed with mean μ and variance σ², it is written as:
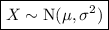
Given:
- Mean μ = 245
- Standard deviation σ = 54
Therefore, if the scores on a standardized exam are normally distributed:
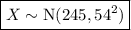
where X is the score on the exam.
Converting to the Z distribution
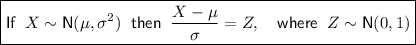
Part (a)
If Bailey scores higher than 90% of all the other people taking the exam, to calculate his score, we need to find the value of a for which P(X > a) = 90%:
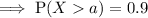
Method 1
Transform X to Z:
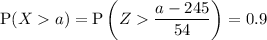
If using z-tables:
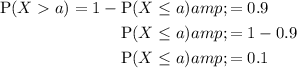
According to the z-tables, when p = 0.1000, z = 1.2816
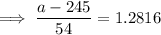
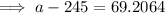
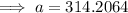
Method 2
Calculator input for "inverse normal":
xInv = 314.2037885...
Therefore, Bailey's approximate score was 314 (nearest whole number).
Part (b)
To calculate the percent of people taking the exam who scored between 200 and 300, we need to find P(200 < X < 300).
Calculator input for "normal cumulative distribution function (cdf)":
- Upper bound: x = 300
- Lower bound: x = 200
- μ = 245
- σ = 54
⇒ P = 0.6434558166...
⇒ P = 64.34558166...%
Therefore, approximately 64% (nearest whole percent) of people taking the exam scored between 200 and 300.