Answer:
2.5 atm
Step-by-step explanation:
To find the original pressure of the gas, you need to use the Combined Gas Law. The corresponding equation is:
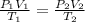
In this equation, "P₁", "V₁", and "T₁" represent the original pressure, volume, and temperature. "P₂", "V₂", and "T₂" represent the new pressure, volume, and temperature.
Before you can plug the given values into the equation and solve for "P₁", you need to convert the temperatures from Celsius to Kelvin (°C + 273 = K).
The final answer should have 2 sig figs like the least accurate given value.
P₁ = ? atm P₂ = 2.0 atm
V₁ = 28 L V₂ = 34 L
T₁ = 45°C + 273 = 318 K T₂ = 35°C + 273 = 308 K
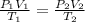 <----- Combined Gas Law
<----- Combined Gas Law
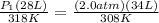 <----- Insert values
<----- Insert values
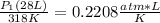 <----- Simplify right side
<----- Simplify right side
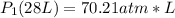 <----- Multiply both sides by 318 K
<----- Multiply both sides by 318 K
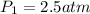 <----- Divide both sides by 28 L
<----- Divide both sides by 28 L