Answer:
The rate law is:
![\displaystyle \text{Rate} & = k[A]^2[B]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/u844r1z6xhfifvklgboxu82ntmtxtmvkr1.png)
Doubling the concentration of C will have no effect on the rate of the reaction.
Step-by-step explanation:
We want to write the rate law for the reaction:
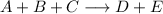
Where the order of A, B, and C are 2, 1, and 0, respectively.
The rate law will have the form:
![\displaystyle \text{Rate} = k [A]^m[B]^n[C]^p](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/axoc28crkidp9pbeqdys6n9inw2heamtcy.png)
Where m, n, and p are their respective order of reactions.
Hence, the rate law is:
![\displaystyle \begin{aligned} \text{Rate} & = k[A]^2[B][C]^0\\ \\ & = k[A]^2[B] \end{aligned}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/ki29lqn5czv778nbku56id158ia9sl7i2j.png)
Because the order of reaction to C is 0, changing its concentration will have no effect on the rate law.