Answer:
The magnitude of the force per unit length is 2.145 x 10⁻⁵ N/m and the direction of the force is outward or repulsive since the current in the two parallel wires are flowing in opposite direction.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given;
distance between the parallel wires, r = 5.0 cm = 0.05 m
current in the first wire, I₁ = 1.65 A
current in the second wire, I₂ = 3.25 A
The magnitude of the force per unit length between the two wires is calculated as follows;
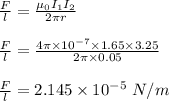
Therefore, the magnitude of the force per unit length is 2.145 x 10⁻⁵ N/m and the direction of the force is outward or repulsive since the current in the two parallel wires are flowing in opposite direction.