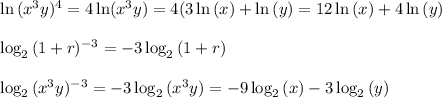Answer:
see below
Explanation:
You want examples of use of the rules of logarithms:
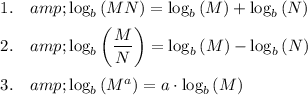
The point of these is that M and N and 'a' and 'b' can be anything. (Generally, 'b' will be a positive number greater than 1.) For the purpose here, we can let M ∈ {x^3y, (1+r)}, N ∈ {(x-4), r/n}, a ∈ {4, -3}, b ∈ {2, e}.
Using these values in various combinations, your examples could be ...
1. Product rule
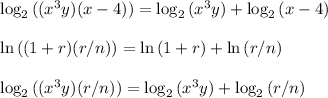
2. Quotient rule
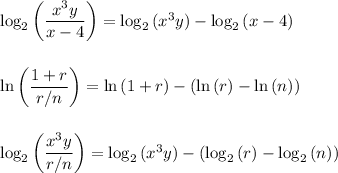
3. Power rule