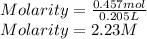Answer:
2.23 M
Step-by-step explanation:
Molarity is given as moles of solute per liter of solution (
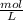 )
)
To solve this problem, the molecular weight (M.W.) of sucrose (
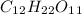 ) must be calculated:
) must be calculated:
C: 12.01
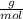
H: 1.01
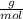
O: 16.00
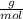
Total M.W.= 12(12.01
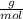 )+22(1.01
)+22(1.01
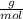 )+11(16.00
)+11(16.00
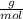 )=342.34
)=342.34
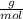
Moles of sucrose can be found through dimensional analysis:
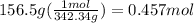
Molarity can be found with: