Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Ginen:
g - free fall acceleration on Earth
M - mass of the Earth
g₁ = g - acceleration of free fall on the planet
M₁ = 2·M - Mass of the planet
______________
R₁ / R - ?
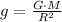
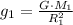
Equate:
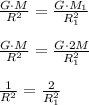
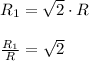
The radius of the planet is √2 times greater than that of the Earth
Планета имеет массу в два раза больше Земли. Насколько больше должен быть радиус планеты для напряженности гравитационного поля, если поверхность планеты будет такой же, как на поверхности Земли?