Answer:
1.53 seconds (2 d.p.)
Step-by-step explanation:
When a body is projected through the air with initial speed u, at an angle of θ to the horizontal, it will move along a curved path.
Therefore, trigonometry can be used to resolve the body's initial velocity into its vertical and horizontal components:
- Horizontal component of u (x) = u cos θ
- Vertical component of u (y) = u sin θ
Because the projectile is modeled as moving only under the influence of gravity, the only acceleration the projectile will experience will be acceleration due to gravity (a = 9.8 m/s²).
Constant Acceleration Equations (SUVAT)
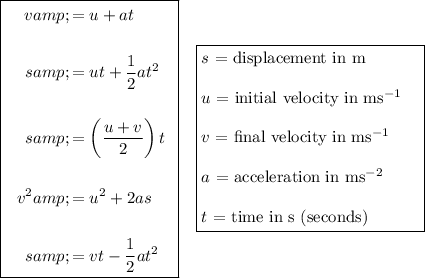
When using SUVAT, assume the object is modeled as a particle and that acceleration is constant.
If an object is thrown at 30 m/s from flat ground at an angle of 30° then:
- Horizontal component of u = 30 cos 30°
- Vertical component of u = 30 sin 30°
When the object reaches its maximum height, the vertical component of its velocity will momentarily be zero.
Resolving vertically, taking up as positive:
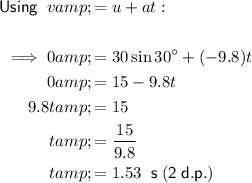
Therefore, the length of time the object takes to reach the highest point of its flight is 1.53 seconds (2 d.p.).