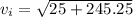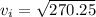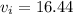Answer:
The Initial Velocity is 16.44 m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
The conservation of energy: As an object falls from rest, its gravitational potential energy (GPE) is converted to kinetic energy (KE). The conservation of energy lets you calculate of the velocity just before it hits the surface.
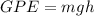
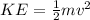
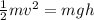
Initial Kinetic Energy + Initial Potential Energy = Final Kinetic Energy + Final Potential Energy.
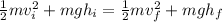
Now we have 6 variables.
- Mass
- Initial Velocity
- Gravity
- Initial Height
- Final Velocity
- Final Height
Lets solve for Initial Velocity.
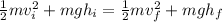
Cancel the common factor
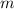 .
.
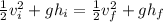
Simplify both sides.
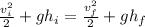
Subtract
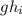 from both sides of the equation.
from both sides of the equation.
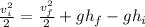
Multiply both sides of the equation by 2.
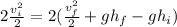
Simplify both sides of the equation.
Cancel the common factor of 2 on the left side.
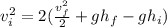
Simplify the right side.
Apply the distributive property.
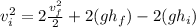
Cancel the common factor of 2.
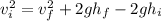
Take the square root of both sides of the equation to eliminate the exponent on the left side.
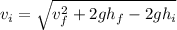
We are given
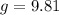
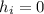
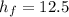
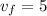
Substitute our values into the equation.