Answer:
Approximately
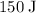 (
(
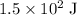 ) assuming that no other force is acting on the ball.
) assuming that no other force is acting on the ball.
Step-by-step explanation:
The net impulse on an object will be equal to the change in the momentum.
Under the assumptions, the force from the racket is the only force on the ball. Since this net force is constant, multiplying this force
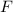 by the duration
by the duration
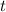 of contact will give the value of the impulse:
of contact will give the value of the impulse:
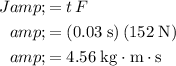 .
.
Note the unit conversion:
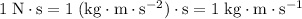 .
.
If an object of mass
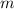 is travelling at a velocity of
is travelling at a velocity of
 , the momentum of that object will be
, the momentum of that object will be
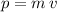 .
.
The momentum of the ball was initially
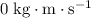 since the ball was initially at rest. Hence, the net impulse of
since the ball was initially at rest. Hence, the net impulse of
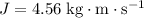 will increase the momentum of this ball to
will increase the momentum of this ball to
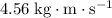 . Divide the momentum of the ball by mass to find the velocity of the ball:
. Divide the momentum of the ball by mass to find the velocity of the ball:
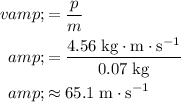 .
.
If an object of mass
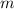 is travelling at a speed of
is travelling at a speed of
 , the kinetic energy of that object will be
, the kinetic energy of that object will be
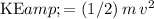 . Since this ball of mass
. Since this ball of mass
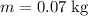 is travelling at
is travelling at
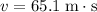 , the kinetic energy of this ball will be:
, the kinetic energy of this ball will be:
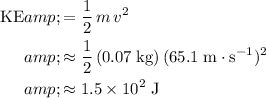 .
.