We need to decide whether the given equations are always or never true for values of x .The given equations are ,
solve out for x,
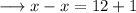
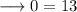
This can never be true. Hence the equation is never true for any values of x.
solve out for x,
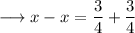
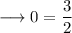
This can never be true. hence the equation is never true for any values of x.
solve out for x,
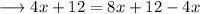
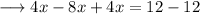
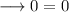
hence this equation is true for all values of x.
solve out for x,
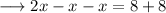
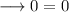
hence the equation is true for all values of x.
solve out for x,
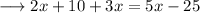
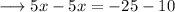
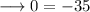
This can never be true. hence the equation is never true for any values of x.
and we are done!