Answer:
pH = 7 ⇒ [H⁺] = 1.0x10⁻⁷ M
pH = 5.6 ⇒ [H⁺] = 2.5x10⁻⁶ M
pH = 3.7 ⇒ [H⁺] = 2.0x10⁻⁴ M
H⁺ concentration in the Hubbard Brook sample is 80 times higher than in unpolluted rainwater.
Step-by-step explanation:
To answer this problem we need to keep in mind the definition of pH:
Meaning that after isolating [H⁺] we're left with:
- [H⁺] =
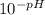
Now we proceed to calculate [H⁺] for the given pHs:
- pH = 7 ⇒ [H⁺] =
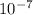 = 1.0x10⁻⁷ M
= 1.0x10⁻⁷ M
- pH = 5.6 ⇒ [H⁺] =
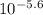 = 2.5x10⁻⁶ M
= 2.5x10⁻⁶ M
- pH = 3.7 ⇒ [H⁺] =
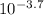 = 2.0x10⁻⁴ M
= 2.0x10⁻⁴ M
Finally we calculate how many times higher is [H⁺] when pH = 3.7 than when pH = 5.6.