Answer:
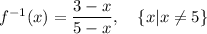
Explanation:
Given function:
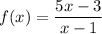
As the given function is a rational function, the domain and range are restricted.
- Domain: (-∞, 1) ∪ (1, ∞).
f⁻¹(x) is the notation for the inverse of the function.
The inverse of a function is a reflection in the line y = x.
To find the inverse of the given function, swap f(x) for y:
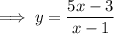
Rearrange the equation to isolate x:
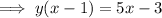
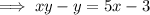
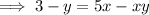
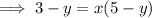
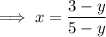
Swap the x for f⁻¹(x) and the y for x:
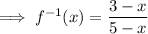
The range of the function is the domain of the inverse function.
Therefore, the domain of the inverse function is restricted:
- Domain of f⁻¹(x): (-∞, 5) ∪ (5, ∞).