Given:
The equation is given as x²+4x = -13.
The objective is to solve the quadratic formula.
Step-by-step explanation:
The equation can be rewritten as,
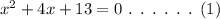
Consider the coefficients of the equation as,
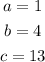
To find solution:
The quadratic formula to find the solutions is,
![x=\frac{-b\pm\sqrt[]{b^2-4ac}}{2a}\text{ . . . . . .(1)}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/ugm5hwawqnphj4h24t9jt1jf6n3rxc9hz6.png)
On plugging the obtained values in equation (1),
![\begin{gathered} x=\frac{-4\pm\sqrt[]{(-4)^2-4(1)(13)}}{2(1)} \\ x=\frac{-4\pm\sqrt[]{16-52}}{2} \\ x=\frac{-4\pm\sqrt[]{-36}}{2} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/ev2p9jt9mb0ieai1128bc0zyif963wvwlo.png)
Since, the discriminant is less than 1, the solutions will be complex roots.
![\sqrt[\square]{(-1)}=i](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/cplvvs0njaojtc2lsjkvzfxpjzxq99olpg.png)
On further solving the above equation,
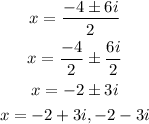
Hence, the solutions of the equation are (-2+3i) and (-2-3i).