The pH relates to the concentration of H+ ions in a solution and the pOH relates to the concentration of OH- ions.
When we mix NaOH and HCl we have a neutralization reaction. To calculate the pH of the solution after the reaction we must determine which is the excess reactant.
The given reaction has the following balanced equation:

From the reaction, we can see that 1 mol of NaOH reacts with 1 mol of HCl.
We will find the moles of each reactant using the definition of molarity:
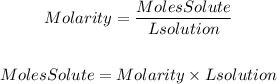
The initial moles of HCl will be:
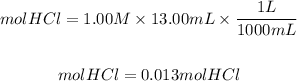
The initial moles of NaOH will be:
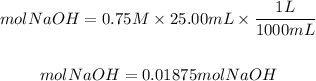
Now, we have more moles of NaOH than moles of HCl, as the ratio NaOH to HCl is 1/1, the limiting reactant will be HCl and the excess reactant is NaOH. It means that after the reaction we will have moles of NaOH that remain. The remaining moles of NaOH will be:
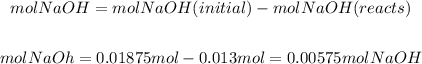
Now, we have to find the concentration of OH ions, to do that we will calculate the final concentration of NaOH. We will assume that the final volume is the sum of the volume of both solutions, so the final concentration of the NaOH solution will be:
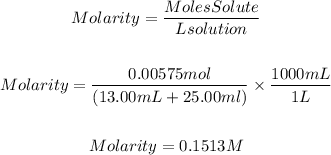
The final concentration of NaOH solution is 0.1513M. As NaOH is a strong acid all the OH ions will dissolve in water, so the OH concentration is the same, 0.1513M.
Now, by definition pOH and pH will be:
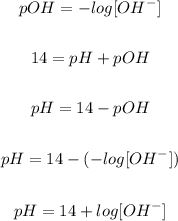
We will replace the [OH-] with 0.1513M:
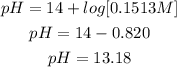
Answer: The pH of the aqueous solution is 13.18