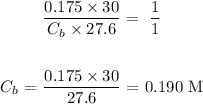Answer:
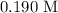
Step-by-step explanation:
Here, we want to get the molarity of the NaOH solution
We start by writing the balanced equation of reaction:
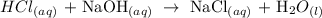
The mathematical formula to use here is that:
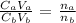
where:
Ca is the molarity of the acid which is 0.175M
Cb is the molarity of the base which we want to calculate
Va is the volume of the acid which is 30 mL
Vb is the volume of the base which is 27.6 mL
na is the number of moles of acid in the balanced equation which is 1
nb is the number of moles of base in the balanced equation which is also 1
Substituting the values, we have it that: