Answer:
22.4 L of carbon dioxide CO2.
Step-by-step explanation:
We need to know what is the maximum volume of carbon dioxide, so here are the steps:
The chemical equation is unbalanced because in the reactants we have 1 mol of hydrogen and in the products, we have 2 moles of hydrogen. The balanced equation would be:
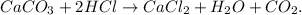
Now, as we know that the limiting reactant is CaCO3, let's find the number of moles of CaCO3. We have to convert 10.0 g CaCO3 to moles using its shown molar mass (100.086 g/mol):
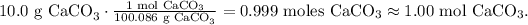
And with this number, we can find the number of moles of CO2 produced. In the chemical equation, you can see that we have 1 mol of CaCO3 reacted and produces 1 mol of CO2, so the molar ratio between CaCO3 and CO2 is 1:1. This means that 1.00 mol of CaCO3 obtained, will produce 1.00 mol of CO2.
The final step is to convert from moles to liters. To find this, we're going to use the STP conditions. In this case, the standard volume of STP is 22.4 L/mol (There are 22.4 L in 1 mol). The conversion is:
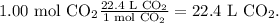
We're going to have 22.4 L of carbon dioxide CO2.