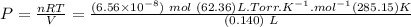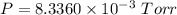Answer
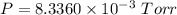
Procedure
The gas can be considered ideal given the temperature conditions. Therefore we can use the ideal gas formula
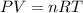
Before substituting the values we need the moles of oxygen
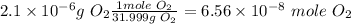
Then we need the gas constant that contains Torr as pressure units
R=62.363577 L.Torr.°K⁻¹.mol⁻¹
We need to convert the volume and temperature into the constant units
T= 12°C+273.15=285.15°K
V=140mL=0.140L
Now we can proceed to substitute the values in the ideal gas equation