Answer:
Explanation:
From the ideal gas law, we know that
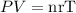
where
P = pressure
V = volume
n = number of moles of gas
r = gas constant
T = temperature.
Know in our case, we know that for a certain number of moles, if V = 0.525 m^3 , P = 485 kPa, then T = -14 celsius. Putting these values (by first converting them to metric units) gives
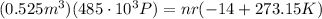
solving for nr gives
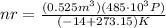
which evaluates to
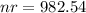
With the value of n*r in hand, we now find the pressure at 42 degrees celsius:
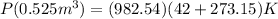
Solving for P ( the pressure) gives
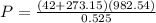
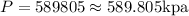
The new gauge pressure is 589.805 kPa.