Answer:
2.24 L of CO2.
Step-by-step explanation:
The balanced chemical equation would be:
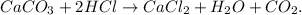
First, let's find the moles of each reactant using their molar mass of them. The conversions are:
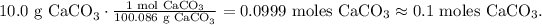
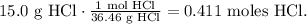
Now, let's see how many moles of CO2 are produced by each reactant. You can see that in the reaction 1 mol of CaCO3 reacted produces 1 mol of CO2, so the molar ratio between these two compounds is 1:1. This means that if we react 0.1 moles of CaCO3, we will obtain 0.1 moles of CO2.
Now, with HCl, you can see that we required 2 moles of HCl to produce 1 mol of CO2. The molar ratio, in this case, is 2:1. This means that 0.411 moles of HCl will produce 0.210 moles of CO2. You can see better like this:
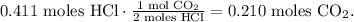
So, the limiting reactant is CaCo3 and we take into account the value of moles of CO2 produced by this reactant (0.1 moles of CO2) because this reactant imposes the limit and because of that, the maximum value of the product. Now, under STP conditions, the volume is 22.4 L in 1 mol, so the conversion from moles to volume is:
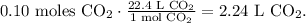
The maximum volume of CO2 would be 2.24 L.