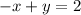To solve this problem it's easier to first find the y-intercept form instead of the standard one, and then re-arrange it in the standard form. The y-intercept form is given below:
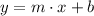
Where "m" is the slope of the line and "b" is the y-intercept. The problem already informed us of the value of "b", therefore we can use the known point to find the value of "m".
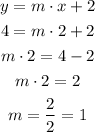
We now have the slope-intercept line as shown below:
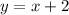
We need to re-arrange it in the standard form, which is shown below:
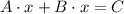
Where A,B and C are constants. So we need to isolate the two variables, x and y, on the left side of the equation.