Answer
ΔHºrxn= 16.2 kJ
Procedure
The first step is to balance the equation. However, it is already balanced.
CH₃COOH → CH₄ + CO₂
For a chemical reaction, the enthalpy of reaction (ΔHrxn) is the difference in enthalpy between products and reactants
We will use the standard enthalpy of formation to calculate the standard enthalpy of reaction:
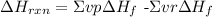
where
vp= stoichiometric coefficient of the product from the balanced reaction
vr= stoichiometric coefficient of the reactants from the balanced reaction
ΔHºf= standard enthalpy of formation for the reactants or the product
For this problem we will have the following:
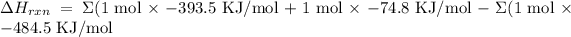
Solving we have
ΔHºrxn= 16.2 kJ