At first, we will find the lengths of LK, Lm, ON, OP, then use them to find the ratios between them
The rule of the distance is
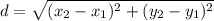
For LK
Since L = (3, 6), K = (1,5.33), then
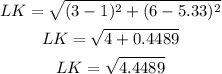
For LM
Since L = (3, 6), M = (5, 6.67), then
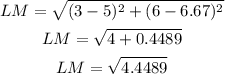
For ON
Since O = (3, 2.59) and N = (5, 4.2), then
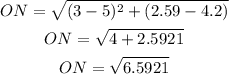
For OP
Since O = (3, 2.59), P = (1, 0.99), then
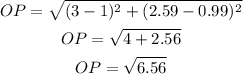
Now let us find the ratios between them

That means, Parallel lines intercept equal parts
By joining MP
We will have Triangle KPM
Since KL = LM ------- Proved using the distance formula
Since LQ // KP ------ Given
Then MQ = QP ------- Using the theorem down
The theorem
If a line is drawn from a midpoint of one side of a triangle parallel to the opposite side, then it will intersect the 3rd side in its midpoint (Q is the midpoint of MP)
Parallel lines intercept equal parts