The coefficient matrix A is,
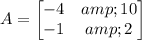
The constant matrix B is,
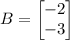
We have the equation,
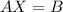
Solving for X, we have,
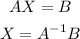
Now, if we have a 2 x 2 matrix of the form,
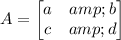
The inverse of this matrix is given by the formula,
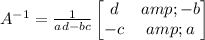
So, let's find the inverse matrix using this formula. Shown below:
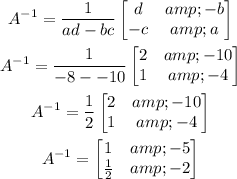
Now, we calculate X,
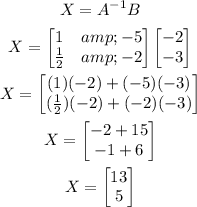
Thus, the solution of the system is >>>
x = 13y = 5