Step 1: Problem
Check the problem on the left-hand side.
Step 2: Concept
Find the center and radius of the circle from the equation of the circle and draw the circle.
Step 3: Method
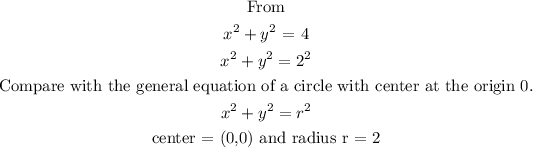
Then find the value of y using Pythagoras theorem.
Opposite = y
Hypotenuse = 2
Adjacent = 1
![\begin{gathered} \text{Opposite}^2+Adjacent^2=Hypotenuse^2 \\ y^2+1^2=2^2 \\ y^2\text{ + 1 = 4} \\ y^2\text{ = 4 - 1} \\ y^2\text{ = 3} \\ y\text{ = }\sqrt[]{3} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/uxbcv55zx6cbn0lkx923vqeilc2xqhe93z.png)
Step 4: Final answer
The line x = 1 intercept the circle at
![(1\text{ , }\sqrt[]{3}\text{ ) and }(\text{ 1 , -}\sqrt[]{3)}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/mm4dij2x16jxwygx66d2lo5ylrerg324ua.png)
Option D is the correct answer.