ANSWER:
0.02182 μC
Explanation:
Given:
Mass (m) = 1.057 g = 0.001057 kg
Length spring (l) = 5 cm = 0.05 m
spring stretch (x) = 1.932 cm = 0.01932 m
spring stretch + beads (x1) = 0.286 cm = 0.00286 m
The first thing to calculate is the value of the spring constant k, just like this:
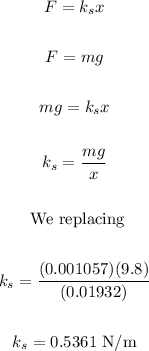
When the charged beads are attached in equilibrium, therefore:

The charge of the beads is 0.02182 μC