The equation for the molarity, or molar concentration, is:
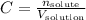
Where C is the molarity, n is the number of moles of solute and V is the volume of solution.
Since we know the molarity and the volume of solution, we can calculate the number of moles of solute:
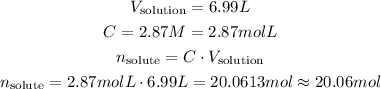
So, there is approximately 20.06 mol in the solution.