The partial pressure of oxygen is calculated as approximately 1.08atm
Partial Pressure
This is the pressure exerted on the containers by the individual gases.
To calculate the partial pressure of oxygen, let's write down our data.
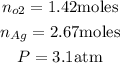
The total numbers of moles is
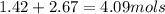
Mole fraction of oxygen is
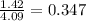
The partial pressure of a gas is calculated as the product between the mole fraction and the total pressure of the gas
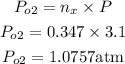
The partial pressure of oxygen is calculated as approximately 1.08atm